Researcher discovered a “more powerful” variant of an elevation-of-privilege flaw for which Microsoft released a botched patch earlier this month.
Attackers are actively exploiting a Windows Installer zero-day vulnerability that was discovered when a patch Microsoft issued for another security hole inadequately fixed the original and unrelated problem.
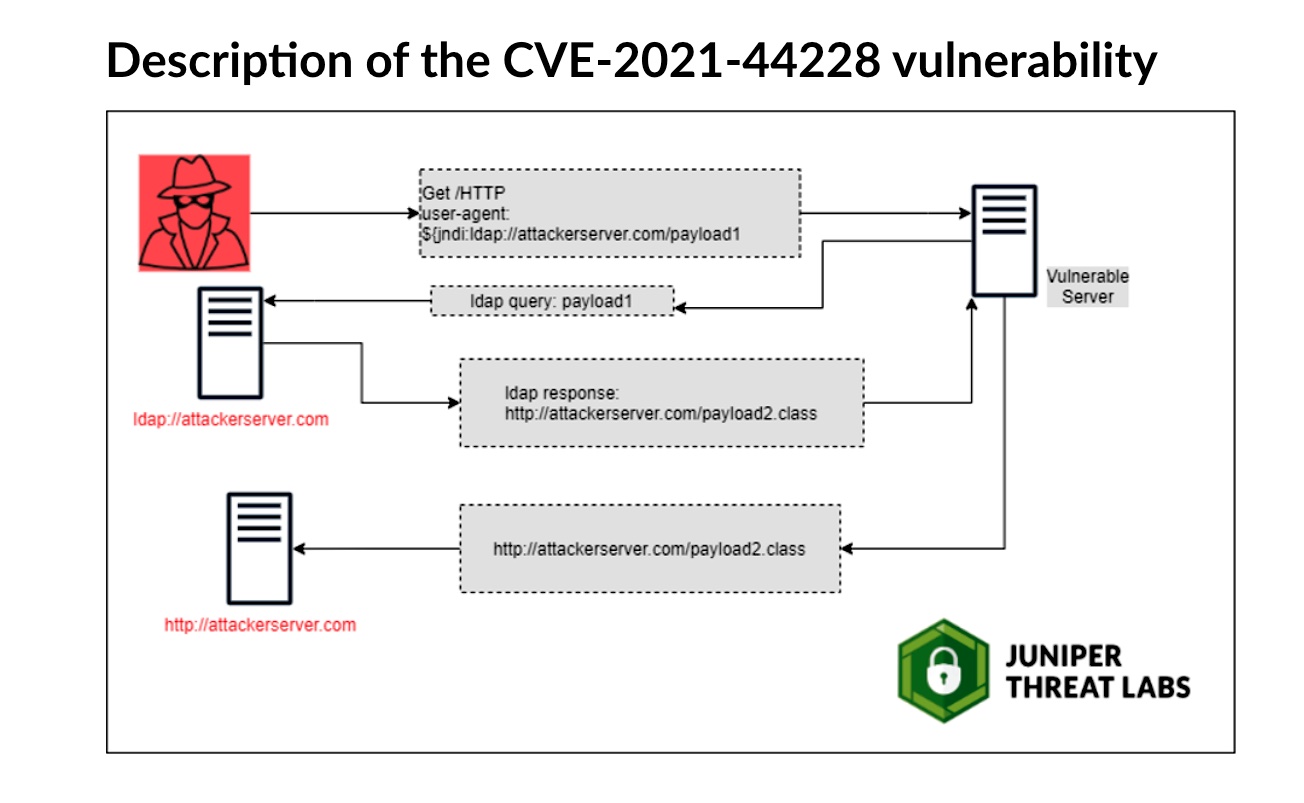
Over the weekend, security researcher Abdelhamid Naceri discovered a Windows Installer elevation-of-privilege vulnerability tracked as CVE-2021-41379 that Microsoft patched a couple of weeks ago as part of its November Patch Tuesday updates.
Attackers Actively Target Windows Installer Zero-Day
Researcher discovered a “more powerful” variant of an elevation-of-privilege flaw for which Microsoft released a botched patch earlier this month.