Aijaa. Olin ymmärtänyt, että erikoisjääkärit sopparilla sekä ETO olisivat meillä PV:n erikoisjoukot.Joo, eihän nää erkkarit mitään erikoismiehiä ole. Kun kerran joutuvat hakeutumaan palvelukseen pääsykokeiden kautta joiden vastaavuus on samaa luokkaa kuin laskuvarjojääkäreillä.
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Rajavartiolaitos
- Viestiketjun aloittaja MoRsE
- Aloitus PVM
tulikomento
Supreme Leader
Aijaa. Olin ymmärtänyt, että erikoisjääkärit sopparilla sekä ETO olisivat meillä PV:n erikoisjoukot.
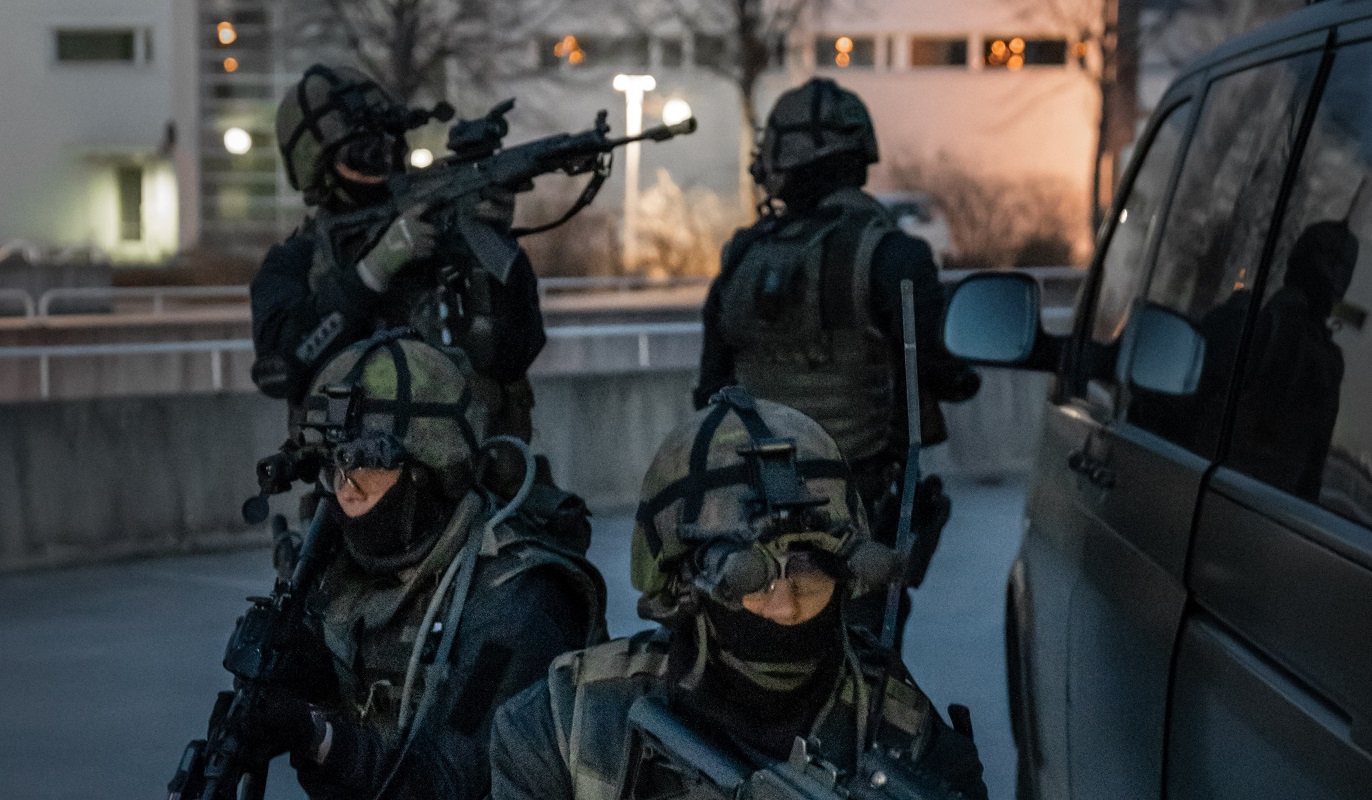
Rajan erkkarit ovat varusmieserikoisjoukko siinä missä PV:n laskuvarjojääkärit ja taistelusukeltajat. Nämä nuoret eivät todellakaan kantele mitään ählämien matkalaukkuja Suomen rajan yli vaan treenaavat jatkuvalla syötöllä sodan ajan toimintaa. Päätehtäviin kuuluu mitä todennäköisimmin mm. harmaan vaiheen aikana toiminta vihollisen erikoisjoukkoja vastaan.

Erikoisrajajääkäriksi Rajalle | Rajavartiolaitos
Kouluttaudu erikoisrajajääkäriksi. Monipuolisessa ja haastavassa koulutuksessa annamme varusmiehille valmiudet toimia Rajavartiolaitoksen erikoisjoukkosotilaana kriisiajan vaativimmissa tiedustelu-, taistelu- ja tukitehtävissä.
Vääpeli
Greatest Leader
Ikävä murtaa tarut, mutta Rajan Erikoisjääkärit on vain paremmin koulutettuja sissejä. Siellä ne vetää pitkin metsiä ja etsii maaleja ja väijyttää vihuja.
"erikoisjoukkosotilaana kriisiajan vaativimmissa tiedustelu-, taistelu- ja tukitehtävissä. " ja "toimintaympäristölle on ominaista valtakunnan rajan läheisyys ja sen erityispiirteet."
"erikoisjoukkosotilaana kriisiajan vaativimmissa tiedustelu-, taistelu- ja tukitehtävissä. " ja "toimintaympäristölle on ominaista valtakunnan rajan läheisyys ja sen erityispiirteet."
Sarlio-Siintola, S. & Tammilehto, T. (2019) Market Analysis. Radars for long distance maritime surveillance and search and rescue operations.
(s. 57)
Tämä laajan näköinen lopputyö tutkii lähtökohtaisesti RANGER-nimistä ratkaisua. Jännästi näkevät Saabin GlobalEyen juuri sen potentiaaliseksi kilpailijaksi.
RANGER on vaikeasti kuvailtava hässäkkä (s. 22).

(s. 57)
Tämä laajan näköinen lopputyö tutkii lähtökohtaisesti RANGER-nimistä ratkaisua. Jännästi näkevät Saabin GlobalEyen juuri sen potentiaaliseksi kilpailijaksi.
Maritime Patrol Aircraft (MPA) is an effective tool for surveillance purposes when discussing of accuracy, areal coverage and selection of surveillance equipment’s. The Saab GlobalEye is the one from MPA class which could be seen as a competitor to RANGER. With approximately four GlobalEye unit and five crew the 24/7/365 operating hours could be possible. The wide range of surveillance systems (air, maritime and surface), the large surveillance area, C2/C4I systems and the capability for remotely operate the surveillance systems makes it considerable option for the customers. Naturally the nature of surveillance from the air makes the GlobalEye marketing extremely challenging for the supplier. (s. 61)
RANGER on vaikeasti kuvailtava hässäkkä (s. 22).
So, what is RANGER and what are the different components that it can offer to the market?
In short, in RANGER there are the first, the OTH radar, which is a High Frequency Surface Wave Radar (HFSWR) system that has the ability to detect targets at very large ranges, beyond the radar horizon. (See sub-chapter 3.2).
Secondly, there is the photonically enhanced PE-MIMO radar, i.e. an innovative radar that complements the OTH radar in detecting targets in close range over several kilometres with high resolution. (See sub-chapter 3.3).
Beyond the two radars, RANGER is much more.
The RANGER platform has its back-end and front-end, as well as the gateways. The Early Warning Engine is the back-end system of the RANGER platform that interfaces with the Uniform Communication Gateway, the Data Fusion module and Machine Learning module, as well as with the Common Information Sharing Environment (CISE) Gateway and the Advanced User Interface. The Early Warning Engine is responsible for early detection of events, data storage and provision of warnings and alerts. It is the core element which is closely interdependent with the Data Fusion and Machine Learning modules of the RANGER platform.
The Data Fusion module’s main role is to take all the available measurements at a particular time step (t), that could be detections from different sensors (radars, existing legacy systems5, and AIS6 data), and fuse them in order to obtain a set of tracks (routes), which are related to the existing targets in the current maritime scene. It performs data association, hybrid tracking and caching. The Machine Learning module will take input measurements from available sensors through the Data Fusion module, and employ machine learning methods to derive conclusions about the characteristics of the detected/tracked vessels and their behaviour. It performs clustering, classification and statistics analysis.
Viimeksi muokattu:
tulikomento
Supreme Leader
Rajamiesten arkea.

 yle.fi
yle.fi
Suomen itärajalla jokakesäinen pesurumba – 190 rajapaalua puhdistuu käsipelissä
Rajavartiolaitoksen työtehtäviin kuuluu rajamerkkien kunnossapito. Kesäisin rajamerkit pestään käsipelin. Ilomantsissa merkkejä on maalla kaikkiaan 191. Lisäksi vesillä olevat rajapoijut tarkistetaan.
tulikomento
Supreme Leader
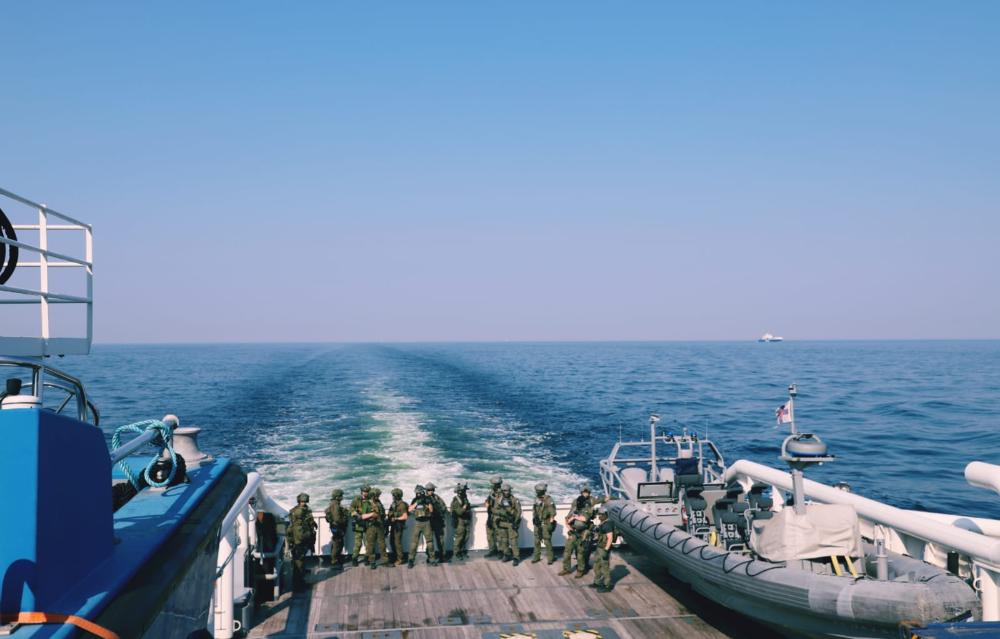
Ollaan hyvässä seurassa kun harjoituksen johtaa Saksan Bundespolizein GSG9.
Mutta miksi ihmeessä harjoituksessa om Kaakkois-Suomen Rajan valmiusjoukkueiden operaattoreita? Eihän heidän tyypillisintä toimialueitta ole laivat.Ollaan hyvässä seurassa kun harjoituksen johtaa Saksan Bundespolizein GSG9.
tulikomento
Supreme Leader
Mutta miksi ihmeessä harjoituksessa om Kaakkois-Suomen Rajan valmiusjoukkueiden operaattoreita? Eihän heidän tyypillisintä toimialueitta ole laivat.
Ei noita erikoismiehiä nyt meillä liikaa ole. Valmiusjoukkueita ei ole kuin SLMV:llä sekä K-SR:llä. Myös Kaakkois-Suomen valmarit treenaavat vesillä oloa, joskin luonnollisesti ei niin useasti kuin Suomenlahden kollegat. Myös K-SR:n valmiusjoukkueen varustukseen kuuluu mm. pikaveneitä. Ja jos kerran harjoituksen johtaa yksi maailman johtavista erikoisjoukko-osastoista, niin lienee hyödyllistä meiltäkin olla mukana niin paljon miehiä oppia saamassa kuin vaan mahdollista.
Juu mutta oudoksuin ettei Suomenlahden miehiä ole. He kun lienevät parhaat spesialistit Suomessa.Ei noita erikoismiehiä nyt meillä liikaa ole. Valmiusjoukkueita ei ole kuin SLMV:llä sekä K-SR:llä. Myös Kaakkois-Suomen valmarit treenaavat vesillä oloa, joskin luonnollisesti ei niin useasti kuin Suomenlahden kollegat. Myös K-SR:n valmiusjoukkueen varustukseen kuuluu mm. pikaveneitä. Ja jos kerran harjoituksen johtaa yksi maailman johtavista erikoisjoukko-osastoista, niin lienee hyödyllistä meiltäkin olla mukana niin paljon miehiä oppia saamassa kuin vaan mahdollista.
tulikomento
Supreme Leader
Juu mutta oudoksuin ettei Suomenlahden miehiä ole. He kun lienevät parhaat spesialistit Suomessa.
Mitä olen juttua kuullut, niin Rajan valmarit loivat suhteita GSG9:n suuntaan jo parikymmentä vuotta sitten. RVL:n väkeä tiettävästi kävi Bonnin Hangelarissa oppia saamassa alan mestareilta. Hyvä että yhteistyö on jatkunut näihin päiviin asti.
"Suomenlahden merivartioston ja Kaakkois-Suomen rajavartioston valmiusjoukkueiden operaattoreita, vartiolaiva Turva, erikoisveneenkuljettajia sekä vartiolentolaivueen helikopteri.'Juu mutta oudoksuin ettei Suomenlahden miehiä ole. He kun lienevät parhaat spesialistit Suomessa.
Tiedotteessa kyllä sanotaan selvästi, että valmiusjoukkueen operaattoreita on molemmista joukkueista. Ja jos mukana on yksikin K-SR.n jantteri, niin silloinhan tiedote pitää kutinsa.
Itse veikkaan valtaosan olevan Suomenlahdelta.
Ps. Mielenkiintoinen tuo erikoisveneenkuljettaja.
Ilmeisesti eri ukkoja kun varsinaiset operaattorit.
tulikomento
Supreme Leader
Ps. Mielenkiintoinen tuo erikoisveneenkuljettaja.
Ilmeisesti eri ukkoja kun varsinaiset operaattorit.
Juttua noista erikoisveneryhmän kuskeista.

Rajamme Vartijat 2/20
tulikomento
Supreme Leader
Tätä rohkenen kyllä epäillä.Myös K-SR:n valmiusjoukkueen varustukseen kuuluu mm. pikaveneitä.
Toisaalta määritelmä "pikavene" on lavea, mutta videollakin nähtävään toimintaan soveltuvaa kalustoa ei Immolanjärvellä taatusti ole
tulikomento
Supreme Leader
Tätä rohkenen kyllä epäillä.
Toisaalta määritelmä "pikavene" on lavea, mutta videollakin nähtävään toimintaan soveltuvaa kalustoa ei Immolanjärvellä taatusti ole
Joo, omasta takaa löytynee RIB-veneitä. Järeämpiä löytyy sitten ainakin Suomenlahden osastolta.
Tässä kuvia tuosta kv-harjoituksesta. Ovat Bundespolizein kuvia.




Vanhana laivamiehenä kiinnostava havaita tuo Kustenwachen laivojen ratkaisut.
Hekokansi takana ja kannen alla "venehangaari".
Molemmilla kyljillä taaveteissa laivan omat veneet, mutta tuonne taakse saataneen ylimääräistä venekalustoa kyytiin..
Tällä kalustolla ei tehdä RVL.n tarvitsemaa hätähinausta /öljyntorjuntaa, vaan selkeästi toisenlainen ajateltu käyttötarkoitus.
Saksalaisten tosin ei paljon tarvitse jäissäkulku ominaisuuksiakaan ottaa huomioon.
Hekokansi takana ja kannen alla "venehangaari".
Molemmilla kyljillä taaveteissa laivan omat veneet, mutta tuonne taakse saataneen ylimääräistä venekalustoa kyytiin..
Tällä kalustolla ei tehdä RVL.n tarvitsemaa hätähinausta /öljyntorjuntaa, vaan selkeästi toisenlainen ajateltu käyttötarkoitus.
Saksalaisten tosin ei paljon tarvitse jäissäkulku ominaisuuksiakaan ottaa huomioon.
Juu. Tässä vielä taustalla ilmeisesti olevan Potsdamin keulatykki lähempää.Tällä kalustolla ei tehdä RVL.n tarvitsemaa hätähinausta /öljyntorjuntaa, vaan selkeästi toisenlainen ajateltu käyttötarkoitus.

Viimeksi muokattu:
mienkoiv
Kapteeni
Mikäs siinä on Niemilammella harjoitellessaTätä rohkenen kyllä epäillä.
Toisaalta määritelmä "pikavene" on lavea, mutta videollakin nähtävään toimintaan soveltuvaa kalustoa ei Immolanjärvellä taatusti ole

