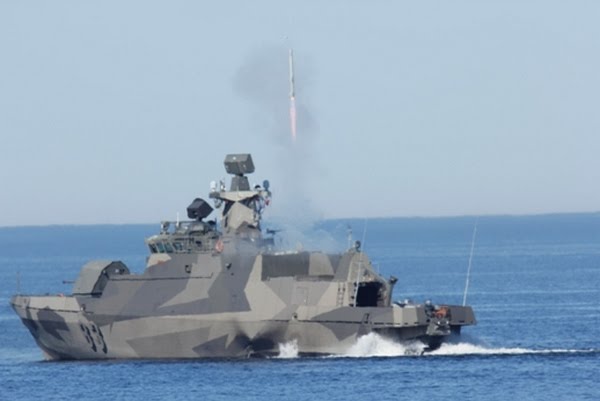
Hamina Class, Finland
Command and control system
The Hamina Class fast attack craft is equipped with TACTICOS (tactical information and command system) combat data system developed by Thales Nederland (formerly Signaal).
The centralised combat management system is based on commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) designs. The system integrates all sub-systems for improving the capability of the craft to simultaneously engage and defeat various types of threats.
ANCS 2000 Combat Management System (EADS)

ANCS 2000 Combat Management System (EADS)
(Source wikipedia.org). The company provides command and control systems for OPVs, corvettes and frigates as well as integrated navigation systems. The Atlas Naval Combat management System (ANCS), our latest-generation combat system, has a modular design that allows it to be adapted to all customer requirements, and has all required interfaces to sensors, shooters and communication facilities. This in turn ensures its integration in a full network-centric warfare (NCW) configuration.
Source aerospacedefence-index.com
MSSR 2000 I-type system from Cassidian identification friend or foe (IFF)
The standard MSSR interrogator for the ASR-Esystem is the MSSR 2000 I. The Interrogator MSSR 2000 I is of modular design. The system fulfills all requirements for a European Mode S Station for elementary surveillance as well as for enhanced surveillance, ground/air data link including de-centralized control in a cluster application.
The Interrogator MSSR 2000 I includes reasonable growth capability to allow the incorporation of new modes or features in the future as a result of its modern technology.
The MSSR 2000 I operates in the following modes which conform to ICAO Annex 10 and STANAG 4193 part 1 – 4 requirements:
- Mode 1,2,3/A,C,4
- Mode S (level 4)
- Mode A/C/S All-Call
- Mode A/C only All-Call
- Mode 1,2,3/A,C mode interlace
- Supermode
The MSSR 2000 I can interrogate in “interlace modus”, (sequences of different modes freely programmable by the user through menu guided input)e.g. M1:M1 or A:A:C or any other desired sequence. The design of the MSSR 2000 I includes the capability to be upgraded to the new military Mode 5.
Source radartutorial.eu
Anti-ship missiles
Armament: 1 × Bofors 57 mm/70 SAK Mk3
2 × 12.7 mm machine guns (NSV)
8 × Umkhonto-IR SAM (Denel)
4 × RBS-15 Mk3 SSM (Saab)
1 × rail for depth charges or mines
Source pbase.com
RBS-15 Mk 3 Anti-ship-missile
Developed as an upgrade of combat proven RBS15 Mk2 missile, the Mk3 was successfully test fired at an FMV (the Swedish Defence Materiel Administration) test range in October 2008. The first missile was assembled outside Sweden in Germany in December that year.
The RBS15 Mk3 is a fire-and-forget, subsonic cruise type missile launched from ships and trucks. The missile can be used for anti-ship missions and land strikes.
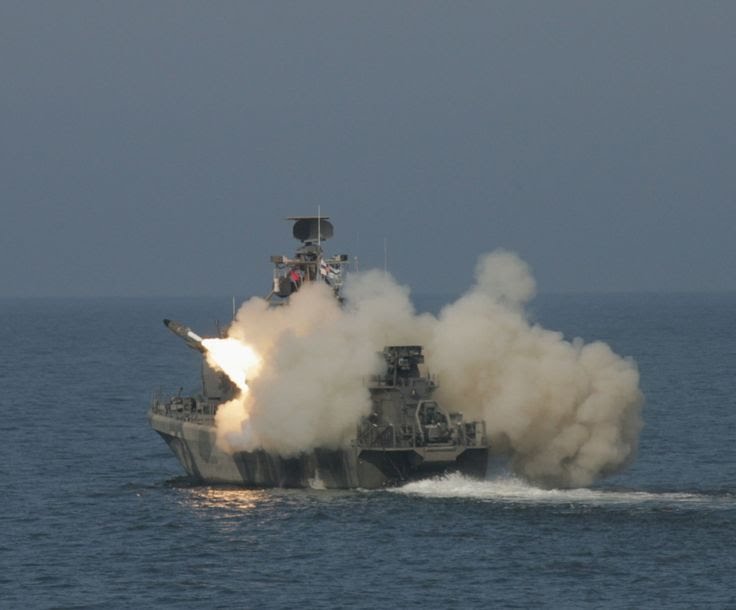 Finnish Hamina Class Missile Boat launching PKR RBS-15 Mk 3. missile s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.comFinnish Hamina Class RBS-15 Mk 3. missile launchers
Finnish Hamina Class Missile Boat launching PKR RBS-15 Mk 3. missile s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.comFinnish Hamina Class RBS-15 Mk 3. missile launchers
The RBS15 Mk3 is available in three versions – ship-launched, truck-launched and air-launched. The ship-launched variant can be installed on small and large sized warships such as fast patrol boats, frigates and corvettes. The missile is easily integrated with the combat management system and can be operated as stand-alone or fully integrated architecture.
The air-to-ship launched version is suitable for modern fighter aircraft. The rapidly deployed truck-launched missile battery provides coastal defence against hostile forces. The highly mobile launch platforms allow the launch of the missile from hidden positions located far away from the coast.
RBS15 Mk3 design and features
RBS-15 Mk 3 Anti-ship-missile @defenceindustrydaily.com
The forward part of the RBS15 Mk3 missile includes guidance and electronics section followed by warhead and fuel section. The rearward section consists of wings and turbojet engine and two parallel booster motors. The missile has cruciform wings that can be retracted during storage.
The missile has a length of 4.35m, fuselage diameter of 0.5m and a wing span of 1.4m. The launch and in-flight weights of the missile are 800kg and 650kg respectively. The RBS15 Mk3 can strike targets within the range of 200km, while travelling at a subsonic speed of 0.9Mach.
RBS15 Mk3 guidance system
The RBS15 guidance and control system includes an inertial navigation system and a GPS receiver, a radar altimeter and a Ku-band radar target seeker. The RBS15 missiles are resistant of enemy countermeasures. Two or more missiles can be programmed to hit the target simultaneously from various directions to better penetrate the air defences of warships.
The missile features low radar cross section and IR signature. It has sophisticated target discrimination and selection capabilities. It is extremely resistant to chaff, active jammers, decoys and other electronic countermeasures (ECM).
The RBS15 Mk3 is a low sea-skimming missile performing unpredictable evasive manoeuvres. The missile increases its thrust in the terminal phase to defeat missiles, guns and close-in weapon systems (CIWS). The missile engagement planning system (MEPS) provides advanced user interface for generating plans for different scenarios.
Warhead and propulsion of RBS15 Mk3 SSM
The missile can be equipped with an optimised heavy HE blast-fragmentation warhead. The highly efficient warhead can penetrate into the hull of any modern vessel.
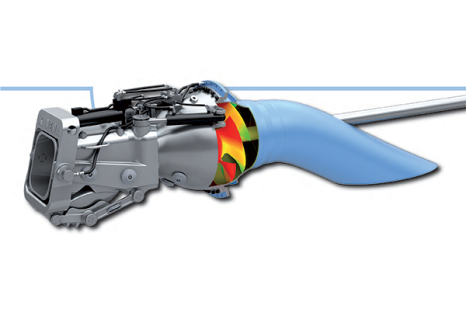
The ship and truck-launched RBS15 Mk3 variants are launched by two booster motors. The missile is powered by TR 60-5 variable-thrust turbo-jet engine developed by Microturbo (a Safran Group company and subsidiary of Turbomeca). The TR60-5 engine incorporating a 3-stage-axial compressor delivers a thrust of 350 to 440daN.
TR60-5 engine
The TR 60-5 family is primarily used for applications of the drone or target drone type.
As such, this engine range powers most of the target drone in service in the united states within the US AirForce AFSAT program and the US NAVY SSAT Program.
Moreover, it perfectly meets the requirements for heavy missile applications such as the RBS 15Mk 3.
Source safran-power-units.com
Data naval-technology.com
MANUFACTURER Saab Bofors Dynamics,
Diehl BGT DefenceSPECIFICATIONS WEIGHT 800 kg
LENGTH 4.33 m
DIAMETER 50 cm
WARHEAD 200 kg
HE blast and pre-fragmented warhead.
DETONATION
MECHANISM
impact or
proximity
ENGINE turbojetWINGSPAN 1.4 m
OPERATIONAL
RANGE
250 km for RBS-15 Mk. III
FLIGHT ALTITUDE sea skimmingSPEED subsonic
GUIDANCE
SYSTEM
inertial,
GPS, terminal
active radar homing (
J band)
LAUNCH
PLATFORM
naval ships, aircraft and land-based
missile launchers
Data wikiwand.com
Umkhonto Surface-to-air Missile
Umkhonto SAM @defenceindustrydaily.com
Umkhonto
Surface-to-air Missile System
Umkhonto (Spear) Missile is an indigenous product, designed, development and manufactured in South Africa. The design of Umkhonto was inspired by the Zulu military commander King Shaka who introduced to his warriors amongst other things, the short Spear, the cow horn formation and the element of surprise. Similarly the Umkhonto missile design includes Stealth (passive IR seeker and low smoke rocket motor) and flexibility (multi target engagement and ability to launch from any position).
The Umkhonto vertical launch Surface to Air Missile (SAM) was developed for the SA Navys Meko A200 class frigates, and has been in service since 2001. Other Navies have also acquired the Umkhonto system, this include amongst others the Finnish Navy. The missile is high-velocity and infrared homing, providing all-round defence against simultaneous attacks from missiles and aircrafts. Although, this is a surface to air missile, it is also capable of taking out stationery surface targets. The Umkhonto was designed with a 23 kg warhead for High-kill probability, unlike other SAM missile systems in its class.
Umkhonto fired from 8-cell vertical launcher on Finnish Navy Hamina-class fast attack craft @lentoposti.fi
System Features
- Multiple-target engagement (up to four targets)
- Ease of integration
- High kill probability (23 kg warhead)
- Countermeasure resistance
- Absence of line-of-sight limitations
- Ease of maintenance (high BIT coverage)
- All-round (360 degree) coverage (with vertical launch)
System Operation
- Target is acquired and tracked by 3-D target acquisition radar
- Missile is launched and flies to a lock-on point, using an on-board inertial navigation subsystem
- IR seeker locks on and missile intercepts target under seeker control
- Continuous updating of target course from surface radar during missile flight, via a telecommand link, to enable engagement of manoeuvring targets.
System Specifications
Physical Characteristics
- Missile length : 3 320 mm
- Missile diameter : 180 mm
- Wingspan : 500 mm
- Launch mass : 135 kg
- Canister length : 3 800 mm
- Canister maximum: 650 mm diameter
Performance Characteristics
- Range : 20 000 m
- Ceiling : 8 000 m
- Maximum Mach No. : 2
- Time of flight to 8 km:18 s
Source deneldynamics.co.za

The latest weapon systems are integrated with the state-of-the-art command system. The vessel is armed with four
RBS-15 mk3 anti-ship missiles each with a range of over 100km. The onboard
Umkhonto-IR surface-to-air missile system can simultaneously engage up to eight aircraft within a 14km range.
Finland’s Hamina-class MLU will include torpedoes: Here
Excerpt
The Finnish Navy’s four Hamina-class missile-capable fast attack craft (FAC) will receive a torpedo fit as part of an overall mid-life upgrade (MLU) programme that will run between 2019 and 2021.
The addition of a torpedo will see the capability return to the Finnish Navy for the first time since the Second World War. Since that time, mines and missiles have made up the bulk of the navy’s capabilities.
Finnish defense minister authorizes Hamina-class upgrades, torpedo system acquisition: Here
Excerpt
Finland’s defense minister on December 19 authorized the country’s defense forces’ logistics command to sign contracts for the upgrade of Hamina-class fast attack missile craft (FAC).
The authorization follows the signing of a letter of intent and a pre-design activities contract with Patria Aviation Ltd. in October this year.
Finnish defense minister Jussi Niinistö has now authorized the logistics command to sign the upgrade contracts with Patria as prime contractor and Swedish company Saab Dynamics which will be delivering its torpedo system to Finland.
Torpedo 47

Torpedo 47 is Sweden’s new lightweight torpedo system for defense against foreign submarines. FMV has contracted Saab AB to develop, produce and integrate the system. The cooperation also includes FOI (the Swedish Defence Research Agency) and the Swedish Armed Forces (SwAF).

There are major challenges in locating and attacking foreign submarines in the Baltic Sea. The factors that contribute to the difficulties are the shallow waters of the Baltic Sea, with a topography and a bottom that challenges the sonar systems. The brackish water, the complexities of the archipelago and the intensive sea traffic are further aggravating factors.
These factors set tough requirements on the torpedo’s ability to:
- Localize and identify submarines
- Navigate under water
- Communicate with the firing platform
The sensor system that will localize and identify submarines is tailor made for the environment in the Baltic Sea. Depending on the local environment the torpedo must have the ability to alter speed, navigate with high accuracy and communicate efficiently with the firing platform.
The new torpedo system is primarily intended for the Swedish submarines and Visby-class corvettes. The system in also prepared for helicopter integration.
Source: fmv.se
There is a
Bofors 57mm gun installed for surface and aerial targets and
two 12.7mm heavy machine guns are also fitted on the craft. The ship can also be fitted with mine rail to detect sea mines.
Bofors 57mm gun
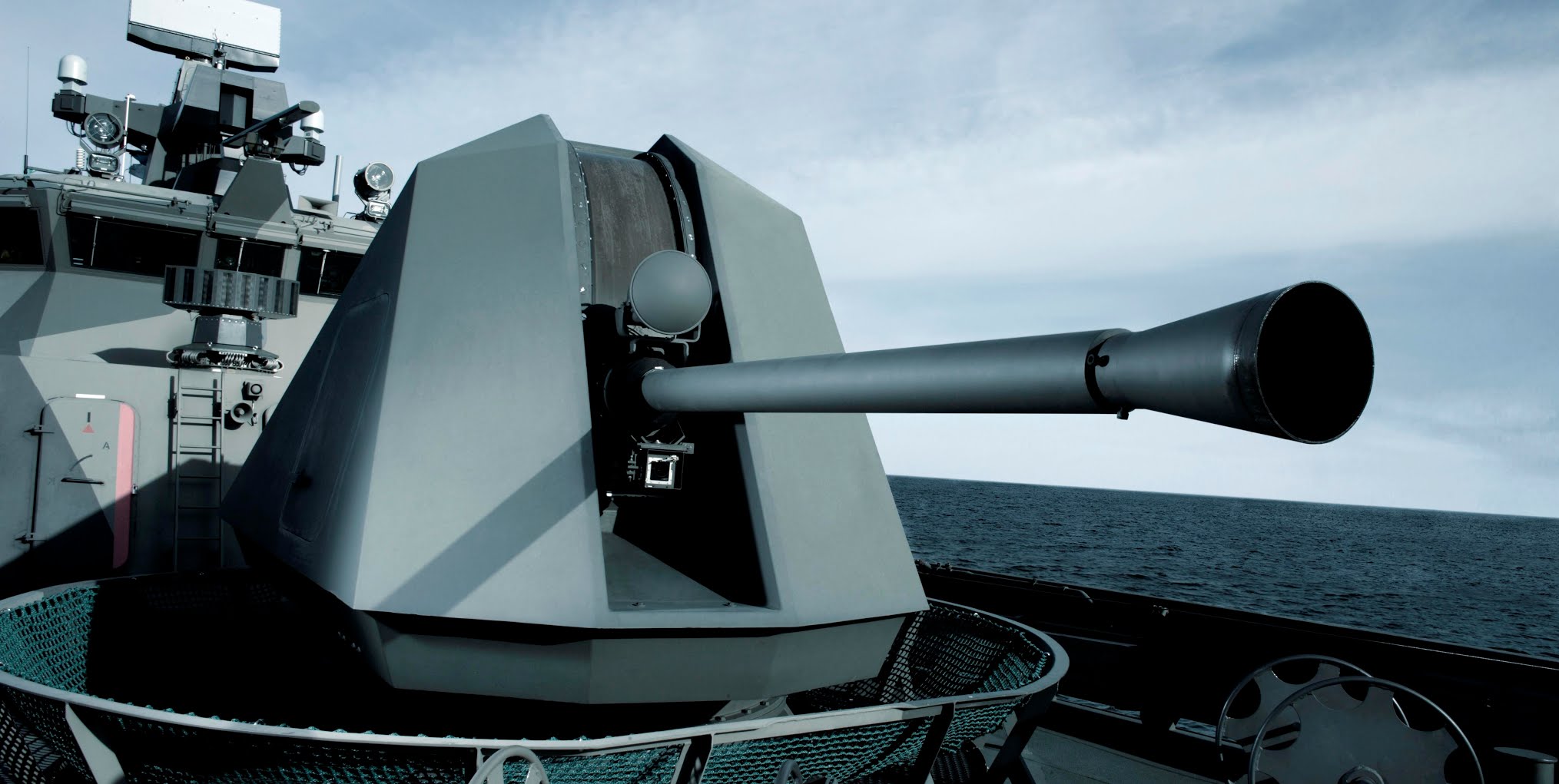 Bofors/BAE Systems 57 mm Mk3 gun – iImage @i.imgur.com
Gun Characteristics
Designation Sweden
Bofors/BAE Systems 57 mm Mk3 gun – iImage @i.imgur.com
Gun Characteristics
Designation Sweden: 57 mm/70 (2.25″) Marks 1, 2 and 3
USN: 57 mm/70 (2.25″) Mark 110 Mod 0 [equivalent to the Mark 3]
Ship Class Used On
- Mark 1:
- Sweden: Hugin, Spica I and Spica II classes
- Finland: Helsinki class
- Mark 2:
- Sweden: Spica III
- Canada: Halifax class
- Mark 3:
- Finland: Squadron 2000 class
- Mexico: Oceànica class
- USCG: Bertholf class (Maritime Security Cutter, Large)
- USN: Freedom (LCS-1) classes
Date Of Design Mark 1: 1964
Mark 2: 1981
Mark 3: 1995
Date In Service Mark 1: 1966
Mark 2: 1985
Mark 3: 1998
Gun Weight N/A
Gun Length oa Rear of breech assembly to forward face of flash hider: 180.2 in (4.577 m)
Bore Length
- Bore length: about 157.1 in (3.990 m)
- Length of gun barrel:
- Without flash hider: 159.25 in (4.045 m)
- With flash hider: 171.06 in (4.345 m)
Rifling Length 139.49 in (3.543 m)
Grooves 24 grooves
Lands N/A
Twist Increasing RH 1 in 46 to 1 in 20
Chamber Volume N/A
Rate Of Fire
- Mark 1: 200 rounds per minute cyclic
- Mark 2: 220 rounds per minute cyclic
- Time to reload 120 rounds: 2 minutes
- Mark 3: 220 rounds per minute cyclic
Typical dispersion of the Mark 3 for elevation (s-value) is 0.4 mrad while that for training (s-value) is 0.4 mrad.
Source navweaps.com
Saab Bound for Naval Grand Slam?: Here
Excerpt
Another interesting inclusion is the Trackfire remote weapon station, with the Hamina now being the third class in the Finnish Navy to receive the RWS. The use of the Trackfire on the Hamina isn’t specified, but the wording in the press release does seem to indicate a single system per ship. As such, while it is possible that two stations per vessel will replace the port and starboard manually operated 12.7 mm NSV heavy machine guns mounted amidships, the likelier scenario is that they will take the place of the main armament. There has been talk (so far unconfirmed?) that the main 57 mm guns (
Bofors Mk 3) of the Hamina vessels will be removed as weight saving measures and transferred to the four Pohjanmaa-class vessels, and this would fit right in. While the Trackfire is usually seen fitted with a heavy machine gun as the main armament, it is capable of holding “lightweight medium calibre cannons”, i.e. weapons up to and including low-pressure 30 mm ones. This is not an unheard of solution, with e.g. the Israeli Typhoon RWS being used with a number of the different
Bushmaster-series of cannons as the main or secondary gun on a number of different naval vessels out there. A 30 mm Bushmaster, the
Mk 44, is already found in Finnish service on the CV 9030 IFV, but before anyone gets too enthusiastic it should be noted that this uses a longer high-pressure round, so there is no synergy to be had. Instead, something like the
M230LF, based on the chain gun found on the Apache helicopter, is the more likely candidate.
Dropping down in calibre from 57 to 30 mm is not necessarily a bad thing, as the main use of the weapon will likely be air defence and intercepting light craft. Modern 30 mm rounds will do
quite some damage against soft targets such as warships as well, though naturally you won’t win a gun fight against a large vessel sporting a 3 or 5 inch gun anytime soon (to be fair, if you find your FAC up against a destroyer at gun range something has likely gone very wrong already at an earlier stage of the battle).
TRACKFIRE – REMOTE WEAPON STATION
 STABILISED INDEPENDENT LINE OF SIGHT (SILOS)
STABILISED INDEPENDENT LINE OF SIGHT (SILOS)
The unique configuration of Trackfire provides a true Stabilised Independent Line Of Sight (SILOS). As the independently stabilised Sensor Module is decoupled from the weapon/s axes (and hence isolated from weapon recoil effects), the operator is able to maintain the line of sight on the target, thereby greatly reducing target acquisition times.
Furthermore, this configuration enables a target to be continuously lased during the engagement sequence; thereby providing a true comprehensive ballistic calculation including 3D target prediction.
FEATURES
The Trackfire RWS provides exceptional capabilities across the full operational spectrum and enhances force multiplication through reliability, superior hit performance and adaptable modularity.
Trackfire consists of the following components:
- Director Unit (DU)
- Human Machine Interface (HMI)
- Gunners Display (GD)
- Fire Control Panel (FCP)
- Control Handle (CH)
- Video Tracker (VT)
MAIN FEATURES
Trackfire RWS provides the hit performance required to engage threats effectively under all conditions. Trackfire has been developed with the operator in mind.
All primary functionality is ergonomically presented on the Human Machine Interface (HMI), ensuring that Surveillance and Target Acquisition (STA) cycles are near instantaneous without the operator having to break visual contact with the Gunners Display (GD).
A dual command facilitates shared capabilities, shorter response times and reduced sensor-to-shooter cycles. Fully prepared for the integration into other platform systems, target and image data can be transmitted within the platform as well as to and from other systems and platforms.
FIREPOWER
A wide range of weapon effects (including complimentary solution such as Non-Lethal effectors) can be mounted, often in combination with one another.
The operator is able to select from the mounted effect with just a switch of a button on the HMI – the embedded Fire Control Computer does the rest. System flexibility also means that both NATO and Eastern Bloc weapons can be mounted.
INTEGRATED SURVIVABILITY
For maximum crew protection, all Trackfire RWS operations can be performed from below armour or deck, thereby increasing their fightability whilst removing them from harm’s way.
Graceful degradation also ensures system functionality in the event of battlefield damage or a malfunction and a reversionary mode ensures that full crew-served operation is still possible.
MOBILITY
Trackfire RWS is designed to meet all operational requirements, ranging from small craft in severe weather conditions to Armoured Fighting Vehicles (AFV) moving at high speed through challenging terrain – all whilst engaging the target with the highest degree of precision
OPTIONAL ENHANCEMENTS
- Smoke Grenade Launchers (SGL)
- Full training suite, ranging from laser-based Integrated Gunnery Trainer (IGT) through to desktop/classroom synthesis training environments
- Dual Command
- Appliquée Armour
- Integration with platform sub-systems, including:
- Battlefield Management Systems (BMS) / Combat Management System (CMS)
- Navigation Systems
- Defensive Aides Suites (DAS)
- Video Distribution System (VDS)
- Health & Usage Monitoring Systems (HUMS)
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
The Trackfire RWS provides exceptional capabilities across the full operational spectrum and enhances force multiplication through reliability, superior hit performance and adaptable modularity. The system consists of the following components:
HUMAN MACHINE INTERFACE (HMI)
Consisting of the Fire Control Panel (FCP), Control Handle (CH) and Gunners Display (GD); the HMI is intuitive to operate. The menu structure has a logical hierarchy to ensure the Operator is able to maintain visual contact of the situation picture via the GD, whilst simultaneously having access to all system primary functionality.
WEAPONS
A wide range of small, medium and heavy Machine Guns, Automatic Grenade Launchers (AGL), lightweight medium calibre cannons, as well as Non-Lethal Effects (NLE) can all be integrated; many of which can be simultaneously mounted to enable a graded effects capability.
SENSOR MODULE (SM)
As a self-contained sub-system, the Sensor Module (SM) provides CCD TV, IR and Laser Range Finder (LRF) channels for the operator. The modular approach allows for a wide range of visual and infra-red sensors to be integrated dependent on User requirements. A wash/wipe capability can also be incorporated.
Source: saab.com








 vai tuliko nyt totuus siitä ohjusten "päivityksestä" esiin...
vai tuliko nyt totuus siitä ohjusten "päivityksestä" esiin...